In this lesson we’ll learn how to calculate the commission earned. What is commission? Commission is the amount of money a salesperson earns on the sale of an item. The formula for commission is Commission=(Sale Price)(Commission Percentage).
Read MoreIn this lesson we will learn how to calculate a percent markup and how it changes the original price of an item. What is a percent markup? Well in retail, a store will buy an item for a certain amount from a manufacturer. In order to make money the store has to add to the price they paid for it and sell it to the customer for more.
Read MoreRemember that the phrase “rationalize the denominator” just means “get the square root(s) out of the denominator”. We already know how to rationalize the denominator if the denominator is just a single square root, and nothing else. But how do we rationalize the denominator when it’s more complicated than just a single square root? In some cases, we can use the conjugate method.
Read MoreThis lesson will cover how to find the power of a negative exponent by using the power rule. If you have two positive real numbers a and b then b^(-a)=1/(b^a). Think of it this way: in order to change the exponent in b^(-a) from -a to positive a, you move the entire value from the numerator to the denominator to get 1/(b^a).
Read MoreIn this lesson we’ll look at how to write the equation of a circle in standard form in order to find the center and radius of the circle. The standard form for the equation of a circle is (x-h)^2+(y-k)^2=r^2, where r is the radius and (h,k) is the center. Sometimes in order to write the equation of a circle in standard form, you’ll need to complete the square twice, once for x and once for y.
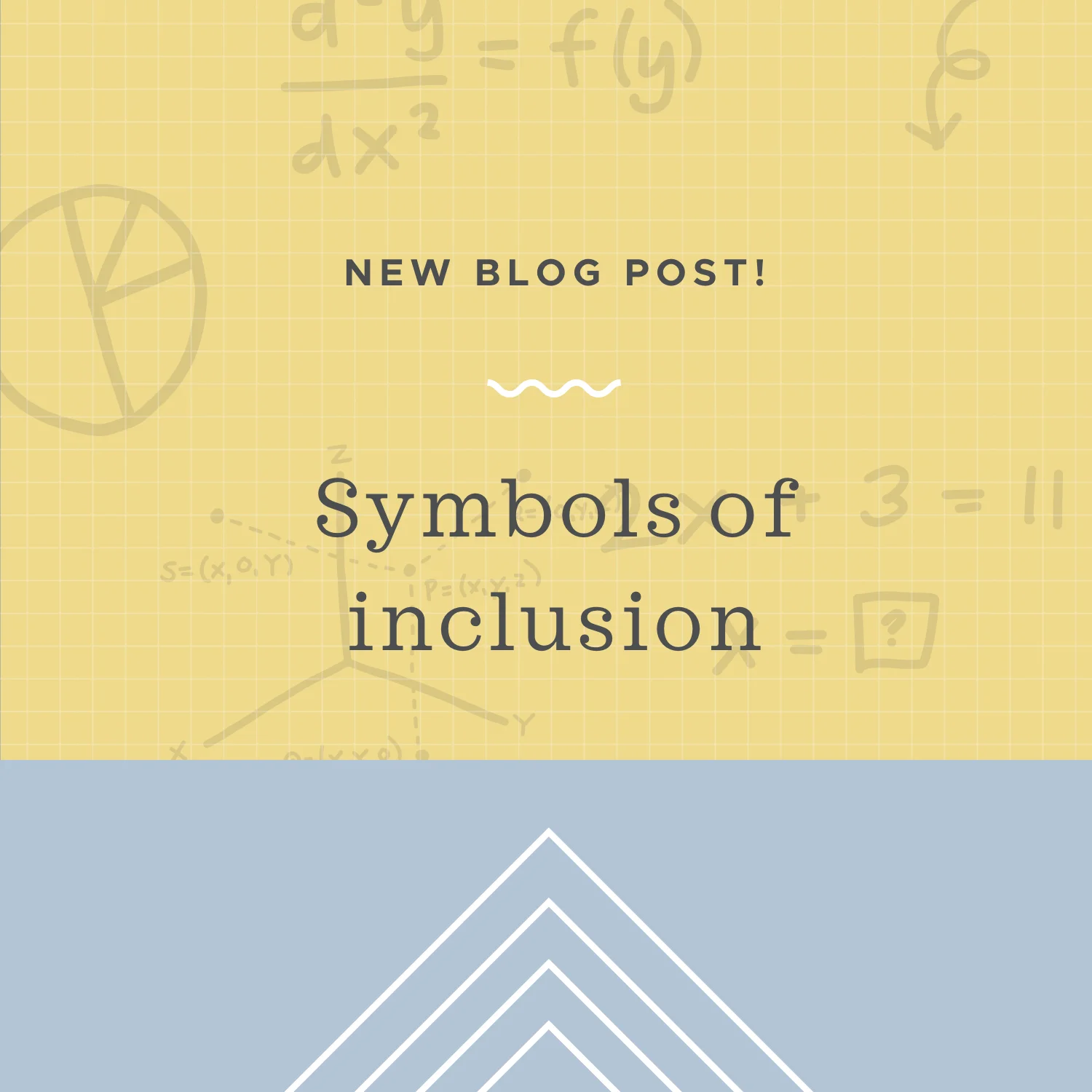
Read MoreSymbols of inclusion group terms together. You’re most familiar with parentheses as a symbol of inclusion, but there are others. Symbols of inclusion are symbols like parentheses, brackets, braces, absolute value bars, and division.
Read MoreIn this lesson you’ll learn how to use the distance formula to calculate the distance between two points. The distance formula is built from the Pythagorean Theorem, so we’ll start with the Pythagorean Theorem, convert it into the distance formula, and then look at how to use the distance formula directly to find the distance between two points.
Read MoreFirst remember that the distributive property is a method you can use to simplify expressions and to multiply the term outside of the parentheses by each term inside the parentheses. It’s the same thing with fractions, just remember to multiply the outside numerator (top) with the numerators of the terms inside parentheses and the outside denominator (bottom) with the denominators of the inside terms.
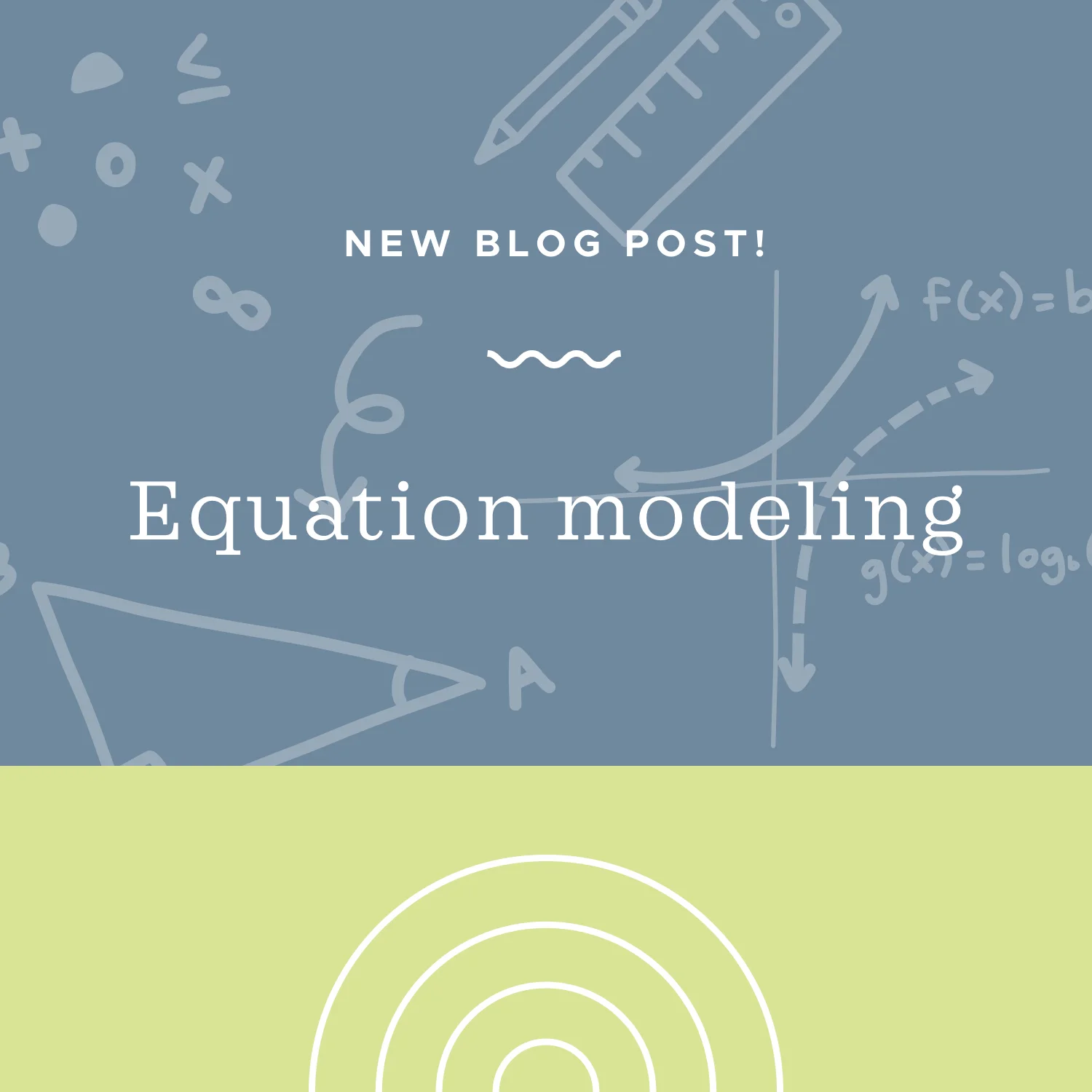
Read MoreIn this lesson we’ll look at how to take a description of an equation in words and transform it into a written equation by using a table. We’ll also look at how to combine existing equations with new information to better model the situation.
Read MoreThe distributive property is a method you can use to simplify expressions, especially when there are variables. To distribute, multiply the term outside of the parentheses by each term inside the parentheses. For instance the distributive property tells us a(b+c)=ab+ac and that a(b-c)=ab-ac.
Read MoreIn this section we’ll talk about how to determine whether a graph represents a one-to-one function. If a relation is a function, then it has exactly one y-value for each x-value. If a function is one-to-one, it also has exactly one x-value for each y-value. The reason we care about one-to-one functions is because only a one-to-one function has an inverse. If the function is not one-to-one, then some restrictions might be needed on the domain of the function to make it invertible. The first way we’ll look at whether or not a function is one-to-one is using the Horizontal Line Test.
Read MoreFunctional notation is a way of writing a function. Traditionally f(x) is how a function is written, but really any variables may be used. The function name is the f or the variable outside of parentheses and the variable used for input is x or the variable that’s inside the parentheses.
Read MoreIn this lesson we’ll look at the definition of an inverse function and how to find a function’s inverse. If you remember from the last lesson, a function is invertible (has an inverse) if it’s one-to-one. Now let’s look a little more into how to find an inverse and what an inverse does.
Read MoreThe Cartesian coordinate system is the structure we use to graph points in two dimensions. Something that has two dimensions is a surface. The Cartesian coordinate system (also called the Cartesian plane, or just “the plane”) is a flat surface (like the cover of a book) that extends forever in all directions.
Read MoreThink of the domain of a function as all the real numbers you can plug in for x without causing the function to be undefined. The range of a function is then the real numbers that would result for y from plugging in the real numbers in the domain for x. In other words, the domain is all x-values or inputs of a function, and the range is all y-values or outputs of a function.
Read MoreIn this lesson we’ll learn about the qualities that make up parallel and perpendicular lines and how to identify them on a graph or in an equation. Remember, opposites are numbers with different signs, as a variable they can be expressed as m and -m (although this doesn’t mean that m is the positive number and -m is the negative number).
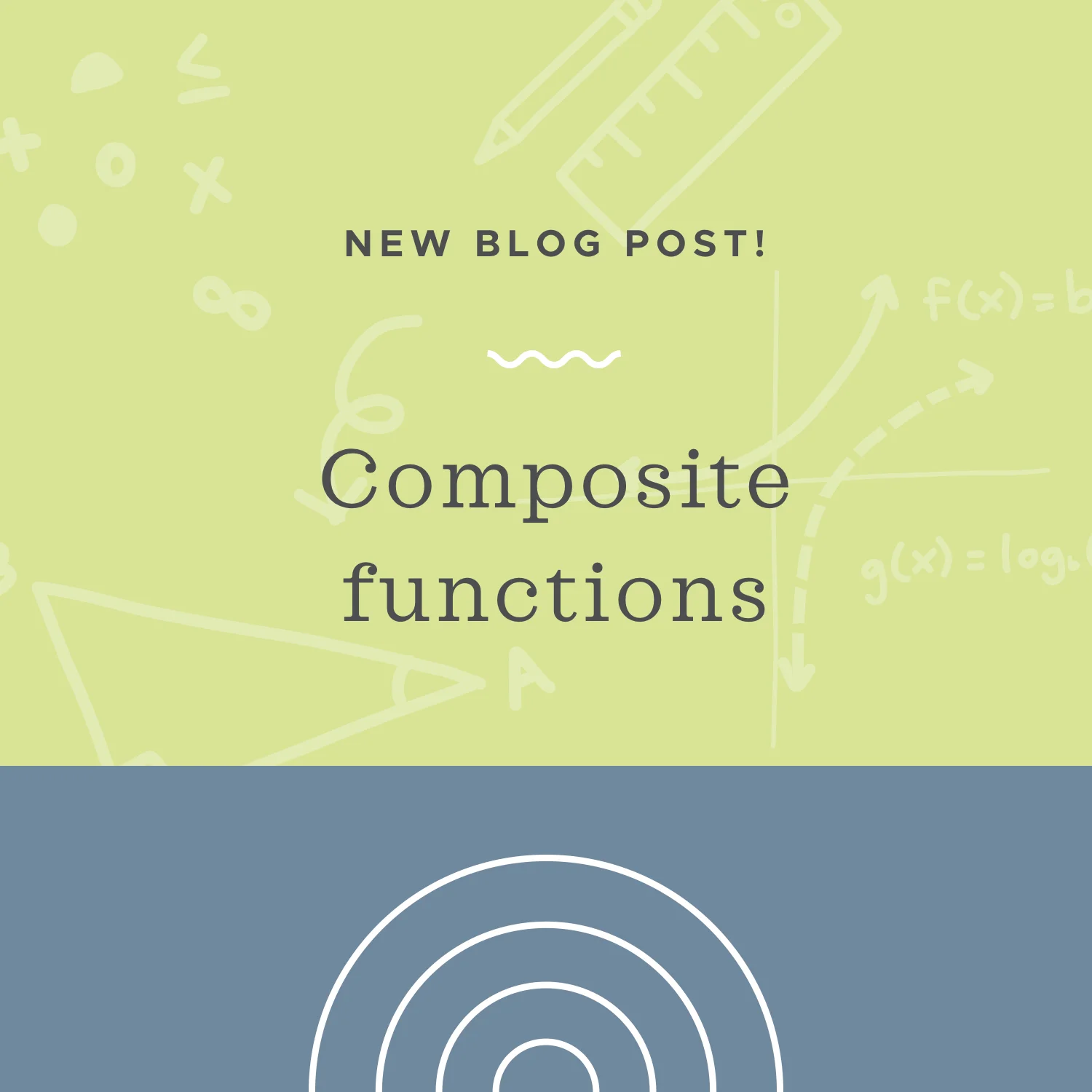
Read MoreIn a composite function, one function is used as a variable in the other function. So to find a composite, we’ll plug one function into the other function, and then simplify the result.
Read MoreThe order of operations is the set of rules that you use to simplify expressions in math. PEMDAS or “Please Excuse My Dear Aunt Sally” are ways to help you remember the order of operations. The order of operations tells us to simplify expressions following this order: Parentheses (all symbols of inclusion), Exponents (powers and roots), Multiplication/Division (from left to right or divide first), then Addition/Subtraction (from left to right or subtract first).
Read MoreIn this lesson you’ll learn how to find the molar mass of chemical compounds given the molar mass of individual atoms, and how to find the molar mass of individual atoms given the molar mass of a compound or molecule.
Read MoreLong division of polynomials uses the same steps you learned for long division of real numbers. It might look different because of the variables but don’t worry, it’s the same thing in disguise. Let’s first review long division. Remember this? You followed a pattern of Divide, Multiply, Subtract, Bring Down.
Read More